ABOUT ABIDJAN CONVENTION
The Abidjan Convention is a treaty signed in 1984 that aims to protect and preserve the marine and coastal environment of the West and Central African region. The convention covers 22 countries, including Cameroon, and addresses a range of issues related to marine pollution, biodiversity conservation, and sustainable development.
Cameroon is one of the signatories of the Abidjan Convention and has been actively engaged in its implementation. The country has taken steps to address marine pollution, including the adoption of laws and regulations to control and manage hazardous waste, oil spills, and other forms of pollution. Cameroon has also established marine protected areas and taken measures to conserve and restore coastal habitats.
ABOUT CAMEROON COASTLINE
In addition to its engagement with the Abidjan Convention, Cameroon has also been involved in other regional and international efforts to protect the marine and coastal environment. For example, the country is a member of the Regional Seas Programme of the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) and has collaborated with other African countries to develop regional strategies for marine conservation and sustainable development.
Overall, Cameroon’s engagement with the Abidjan Convention and other regional and international initiatives demonstrates its commitment to protecting and preserving the marine and coastal environment, which is critical for the country’s economy and the well-being of its people.
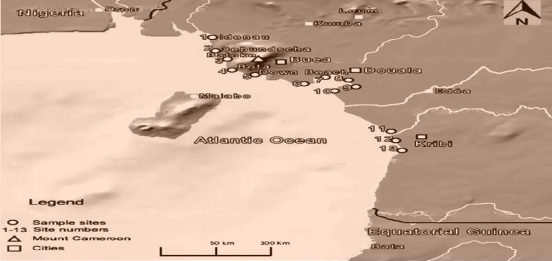
Cameroon is a country located in central Africa that has a coastline along the Gulf of Guinea. The coastline of Cameroon stretches for approximately 402 kilometers (250 miles) and is characterized by a mixture of sandy beaches, rocky cliffs, and mangrove swamps.
The coastline of Cameroon is home to a number of major ports, including the Port of Douala, which is the largest port in Central Africa. Other ports along the coastline include the Port of Limbe, the Port of Kribi, and the Port of Tiko. These ports are important for the country’s economy as they serve as gateways for international trade and commerce.
The waters off the Cameroon coastline are also important for fishing, with a variety of fish species found in the area. The coastline is also home to a number of beach resorts and tourist attractions, including the Limbe Wildlife Centre and the Korup National Park, which is one of the oldest and most biodiverse rainforests in Africa.
